NIM : 11615042
Dasar Teori :
Dalam melakukan tugas-tugas administrasi sistem,
administrator sistem mau tidak mau akan banyak berhubungan dengan tools – tools
pendukung. Tanpa bantuan tool ini pekerjaan administrasi akan sulit dijalankan.
Network Management
Etherman
Tool yang berbasis GUI yang menampilkan
representasi dari komunikasi – komunikasi ethernet secara real time.
Tcp wrapper
Berguna untuk mengontrol siapa saja yang
mengakses sistem. Dapat memproteksi usaha pelanggaran terhadap sistem
Xmotd
Dipakai menuliskan atau menampilkan Message
of the day, untuk setiap user yang login
Samba
Memungkinkan melakukan sharing file antar so
Swatch
program
untuk memonitor log
dig
query server domain
host
memperoleh informasi nama domain
nslookup
tcpdump
mengcapture packet
traceroute
melakukan trace terhadap rute paket IP dari
sistem ke sistem tujuan
sniffit
tools memberikan informasi detail ttg semua
traffic jaringan
ssl
nmap
netstat
Ada beberapa command pada linux yang
dipakai untuk melakukan konfigurasi dan
troubleshooting jaringan :
Layer phisik
1.
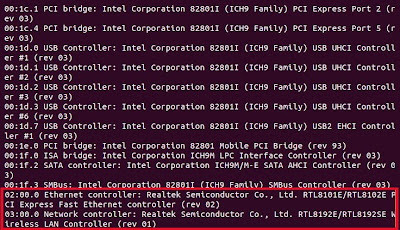
lspci
Merupakan tools yang berada pada layer 1, dipakai untuk mengecek
apakah interface jaringannya sudah terpasang atau belum. Apabila ditemukan
Network controller atau Ethernel controller, artinya perangkat jaringan sudah
siap digunakan.
2.
mii-tool
Untuk melihat apakah linknya sudah ada atau belum
3.
dmesg | grep eth
Untuk mengecek ethernet card ada apa belum
Layer datalink
1.
arp
Merupakan tools yang dipakai untuk melihat alamat NIC dari komputer
yang terkoneksi secara langsung dengan kita.
Layer IP
1.
ifconfig
Command yang dipakai untuk melihat interface dan alamat yang
diberikan ke interface tersebut
2.
route
Memeriksa tabel routing, menambah dan menghapus tabel routing
3.
ping
Memeriksa koneksi dengan protokol ICMP
4.
traceroute
Memeriksa tahapan koneksi
5.
mtr
Command gabungan ping dan traceroute
6.
netconfig
Command untuk konfigurasi ip secara permanen
Layer
Transport
1.
Netstat
Untuk mengetahui port berapa saja yang
terbuka untuk koneksi pada PC
Tugas Pendahuluan
Jelaskan cara penggunaan command dibawah ini beserta option yang digunakan dan artinya
1. lspci
2. mii-tool
3. arp
4. ifconfig
5. route
6. ping
7. traceroute
8.
mtr
9. netstat
10. netconfig
Cara Penggunaan Command di atas
1. lspci - list all PCI devices
contoh : lspci -v (akan menampilkan informasi rinci tentang semua perangkat.)
contoh : lspci -v (akan menampilkan informasi rinci tentang semua perangkat.)
2. mii-tool - view, manipulate media-independent interface status
contoh : mii-tool -V (Menampilkan program version information.)
contoh : mii-tool -V (Menampilkan program version information.)
3. arp - manipulate the system ARP cache
contoh : arp -n (shows numerical addresses instead of trying to determine symbolic host, port or user names.)
contoh : arp -n (shows numerical addresses instead of trying to determine symbolic host, port or user names.)
4. ifconfig - configure a network interface
contoh : ifconfig eth0 (yang berarti configurasi network interface pada ethernet 0)
contoh : ifconfig eth0 (yang berarti configurasi network interface pada ethernet 0)
5. route - show / manipulate the IP routing table
contoh : route add -net 192.56.76.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 dev eth0 (yang berarti menambahkan route ke network 192.56.76.x lewat "eth0")
6. ping - send ICMP ECHO_REQUEST to network hosts
contoh : ping -b (Allow pinging a broadcast address.)
7. traceroute - print the route packets take to network host
contoh : traceroute -w (Set the time (in seconds) to wait for a response to a probe (default 5 sec.))
8. mtr - a network diagnostic tool
contoh : mtr -n (Use this option to force mtr to display numeric IP numbers and not try to resolve the host names.)
9. netstat - Print network connections, routing tables, interface statistics, masquerade connections, and multicast memberships
contoh : netstat -r (Display the kernel routing tables.)
10. netconfig - A text-based tool for simple configuration of ethernet devices.
Hasil Pecobaan
1. Jalankan perintah “dmesg | grep eth”, catat dan analisa hasilnya. Jika tidak ada keluaran konfirmasikan ke dosen/asisten praktikum.
7.
Jalankan perintah
route –n, catat hasilnya.
contoh : ping -b (Allow pinging a broadcast address.)
7. traceroute - print the route packets take to network host
contoh : traceroute -w (Set the time (in seconds) to wait for a response to a probe (default 5 sec.))
8. mtr - a network diagnostic tool
contoh : mtr -n (Use this option to force mtr to display numeric IP numbers and not try to resolve the host names.)
9. netstat - Print network connections, routing tables, interface statistics, masquerade connections, and multicast memberships
contoh : netstat -r (Display the kernel routing tables.)
10. netconfig - A text-based tool for simple configuration of ethernet devices.
Hasil Pecobaan
1. Jalankan perintah “dmesg | grep eth”, catat dan analisa hasilnya. Jika tidak ada keluaran konfirmasikan ke dosen/asisten praktikum.
2. Lepaskan kabel jaringan,
lakukan perintah mii-tool
3. Pasangkan lagi kabel
jaringan dan lakukan perintah mii-tool
4. Catat hasil dari
perintah “lspci” sebelum dan sesudah melepas kabel
5. jalankan
perintah ”arp –a” dan catat hasilnya , buka beberap terminal baru lagi dan
jalankan perintah ”ping no_ip_tujuan” ke beberapa komputer sebelah (tanya nomor
IP tersebut ke teman). Pada terminal pertama lakukan perintah arp –a sekali
lagi . Catat hasilnya dan bandingkan dengan hasil arp yang pertama, analisa
hasilnya
6.
Jalankan perintah
”ifconfig”, catat hasilnya.



No comments:
Post a Comment